Glenn Luther Martin was one of the earliest pioneers of American aviation, an aircraft designer, and a manufacturer. He founded the Glenn L. Martin Company, a leading producer of military aircraft. The legacy of this Los Angeles aviation designer lives on today within the structure of the giant Lockheed Martin. La-future provides more details on Glenn Luther Martin’s contribution to the development of aviation in California and Maryland, which changed the course of 20th-century history.
Early Years and First Steps in the Sky
The future aircraft designer was born in Macksburg, Iowa, to Minta and Clarence Martin. When Glenn was 2 years old, the family moved to Salina, Kansas, and at age 6, he became interested in kites. Despite being mocked by his peers, he manufactured kites, and people paid him 25 cents for them. His mother’s kitchen was successfully transformed into a small factory to produce a larger quantity of products. This was Glenn Martin’s first business idea.
Later, he studied at Kansas Wesleyan University in Salina. In 1933, he earned an honorary Bachelor of Science degree.
Subsequently, his passion for kites transitioned to the Wright brothers’ airplane. In 1909, he managed to build his own aircraft based on the Curtiss June Bug. Unfortunately, this model was destroyed after its very first test flight. While he admired Curtiss, his first successful plane is usually referred to as the Martin No. 1, not simply a copy of the June Bug. The next attempt proved more successful. He was assisted by his mother, who held a lamp during the construction of his first aircraft models.
A flight on May 10, 1912, proved exceptionally successful. Glenn Martin flew a self-built seaplane from Newport Bay, California, to Avalon on Catalina Island. Then the seaplane returned across the channel, breaking the previous English Channel record for over-water flight (total distance – 68 miles, and the path from Newport to Avalon took 37 minutes). For this significant achievement, the aircraft designer received a $100 prize.
In 1913, Glenn Martin was not as fortunate. The seaplane hit the waves at high speed and low altitude, after which it capsized. Martin managed to escape.
Founding of the Glenn L. Martin Company in Los Angeles
In 1912, Glenn Martin built an aircraft manufacturing plant in Los Angeles. An old Methodist church was chosen for this purpose.
Financing the business required additional sources of income, so Martin began engaging in stunt flying activities at fairs and local airfields.
Another interesting opportunity to promote aircraft, which the founder utilized, was filming the 1915 production “A Girl of Yesterday.” In this American silent comedy, the lead role of an was played by the young girl star Mary Pickford, who also wrote the script. Glenn Martin did not expect filmmaking to be so difficult. His duties included not only flying the plane but also a kiss scene with legendary Hollywood screenwriter Frances Marion. To perform this scene, he needed all his courage and persuasion from Paramount co-founder Adolph Zukor.

The Era of Major Contracts and Innovations
Glenn Martin was never just an “office” engineer—he was a true fan of the sky. At a time when aviation was considered a dangerous toy, he personally proved the opposite. His 1912 record became a real sensation: Martin flew 66 miles over water from Newport Bay to Catalina Island in a self-built seaplane. Imagine: an open cockpit, the roar of the engine, and only the endless ocean under the wings. It was this desperate journey that finally made the military take aviation seriously.
When World War I began, Martin realized:
“The future belongs to heavy aviation”
Thus appeared the Martin MB-1—a powerful biplane that became the “gold standard” for American bombers. Its successor, the Martin MB-2, changed the rules of war entirely. It was these aircraft during Billy Mitchell’s legendary tests that proved the incredible: aviation is capable of sending huge battleships to the bottom, forever changing naval battle strategy.
Real triumph came in 1932 when Martin received the Collier Trophy—the “Oscar” of the aviation world. The occasion was the revolutionary Martin B-10. This was the first all-metal bomber that developed such speeds that the fighters of that time simply could not catch it. This aircraft became not just an engineering victory, but a final confirmation that Martin was a leader dictating fashion in the American sky.

Influence on the Engineering School
Glenn L. Martin went down in history as the “teacher of giants,” turning his company into a real talent foundry. His competitors and contemporaries were future legends as William Boeing, Donald Douglas, and Lawrence Bell, who subsequently founded their own aircraft empires.
During the years of World War II, Martin became a key supplier of U.S. air power, developing the legendary high-speed B-26 Marauder bomber and the Martin PBM Mariner maritime patrol aircraft, which became indispensable in the fight against submarines. His engineering school not only ensured victory in the air but also laid the foundation for a global technological leap and post-war innovations in the aerospace industry.

Interesting History of Lockheed Martin
The history of Lockheed Martin is not just a chronicle of corporate success, but a story of how the impossible became everyday. Imagine how drastically our world has changed over these hundred years.
- When aviation was taking its first timid steps, America was completely different. In 1912, there were only 220 kilometers of paved roads in the entire huge country, and the Eiffel Tower in Paris still remained the tallest structure on the planet. The first planes of that time resembled a modern cyclist in speed—barely reaching 48 km/h.
- It is hard to believe, but the foundation of the future empire was not laid in ultra-modern laboratories. It all started with pure enthusiasm: one dreamer crafted blueprints within the walls of an old rented church in Santa Ana, and two talented mechanics in an ordinary San Francisco garage assembled their first hydroplanes. It was from this “garage” spirit that the legend was born.
- Lockheed Martin did not just build equipment—it “ignited” hearts. The company became the engine of the space race, allowing humanity to break free from Earth’s gravity. Thanks to their satellites, today we do not just forecast the weather, but literally look into the past of the Universe: we see the birth of stars and hear the echoes of the Big Bang.
- Having passed through the fires of wars and the industrial boom, the company managed to tame the power of “ones and zeros.” Today, it feels confident in the era of artificial intelligence and cyber defense, where complex state missions are performed using code and digital innovations.
In 2012, celebrating its 100th anniversary, the company released a touching video summarizing this incredible journey—from canvas wings to interstellar travel.
Legacy and Commemoration of Glenn L. Martin
| Category | Object / Event | Location | Meaning and Description |
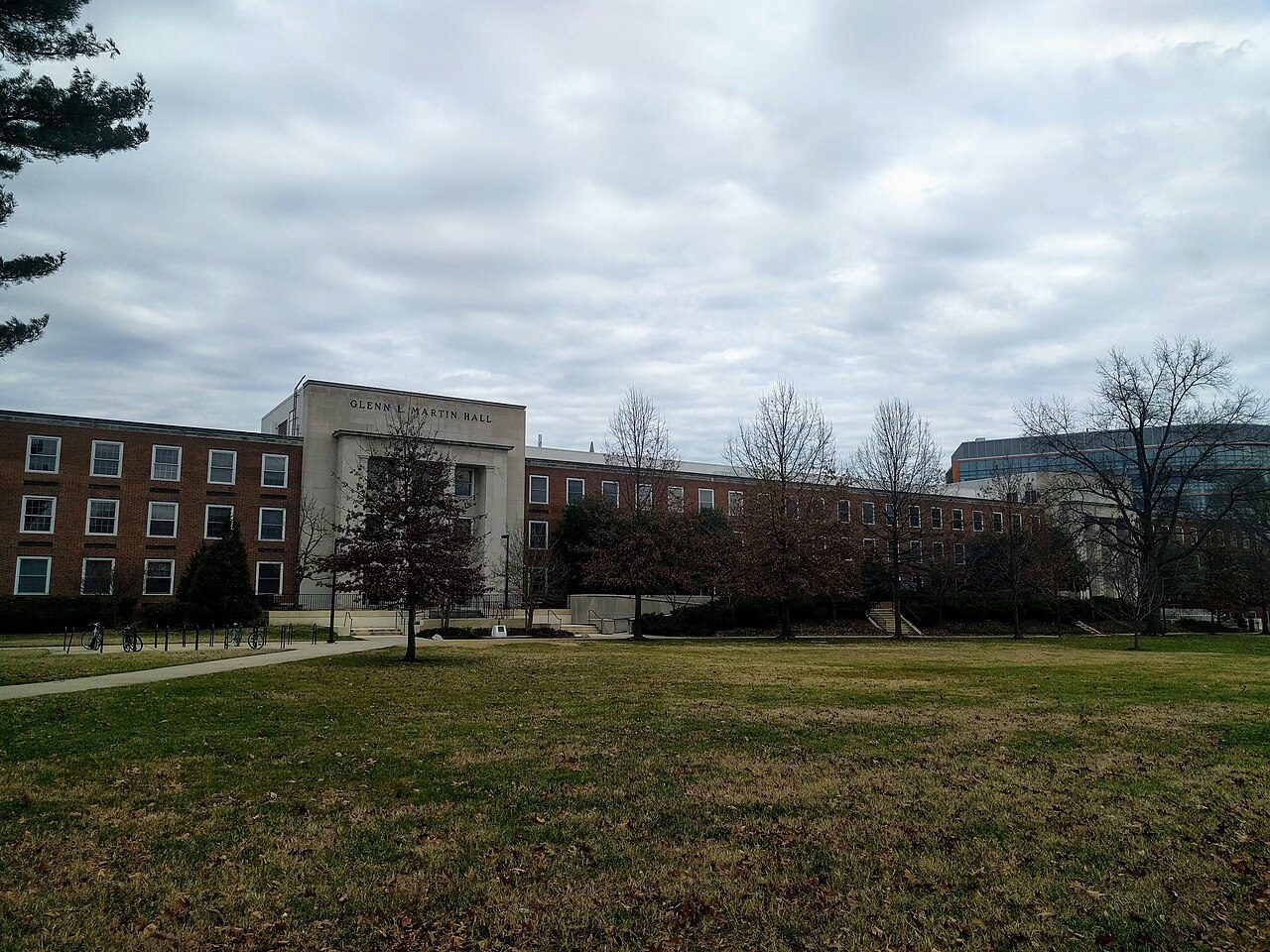
| Education and Science | Glenn L. Martin Hall | University of Maryland, College Park, USA | The main academic building housing the Department of Aerospace Engineering. Built thanks to Martin’s financial support. |
| Education and Science | A. James Clark School of Engineering | College Park, Maryland | Martin allocated funds for the creation of the Institute of Technology, which became the scientific core of this prestigious school. |
| Research | Glenn L. Martin Wind Tunnel | College Park Metro | A large wind tunnel used for testing aircraft, cars, and architectural models. |
| Ecology | Martin National Wildlife Refuge | Smith Island, Maryland | A nature reserve of 2,569 acres (1,040 ha), donated by Martin to protect migratory birds and wildlife. |
| Sports | AAABA Tournament | Johnstown, Pennsylvania | All-American Amateur Baseball Association, founded by Martin in 1945. The tournament is held annually to this day. |
| Education | Glenn L. Martin Elementary School | Santa Ana, California | An elementary school named after the designer in the city where he began his aviation career. |
| Halls of Honor | National Aviation Hall of Fame | Dayton, Ohio | Inducted in 1966 for outstanding contributions to the development of the aviation industry and technologies. |
| Halls of Honor | International Air & Space Hall of Fame | San Diego, California | Inducted in 1977 as one of the key pioneers of the aerospace era. |
| Culture | “Building Bridges” Stamp Series | USA (USPS) | A special philatelic series for the 110th anniversary of his historic transoceanic flight to Catalina Island. |
| Music | “Break Free on Wings of Music” | World Premiere | A musical work by Kendall Ross Bean, written specifically to honor the memory of Martin and his 1912 flight. |
Thus, Glenn L. Martin went down in history as a talented aircraft designer and a visionary entrepreneur. His path from a small workshop in Los Angeles to global leadership is the embodiment of the “American dream” and technical progress. It can be assumed that in every engineering development in the aerospace field, there is a piece of Glenn L. Martin’s innovative spirit.

Sources:
- https://www.lockheedmartin.com/en-us/news/features/history.html
- https://grokipedia.com/page/Glenn_L._Martin
- https://airandspace.si.edu/collection-objects/pin-lapel-national-aeronautic-association-glenn-l-martin/nasm_A19590118001
- https://www.latimes.com/archives/la-xpm-2003-sep-28-me-then28-story.html#
- https://www.b26.com/page/from_barnstorming_to_bombers.htm